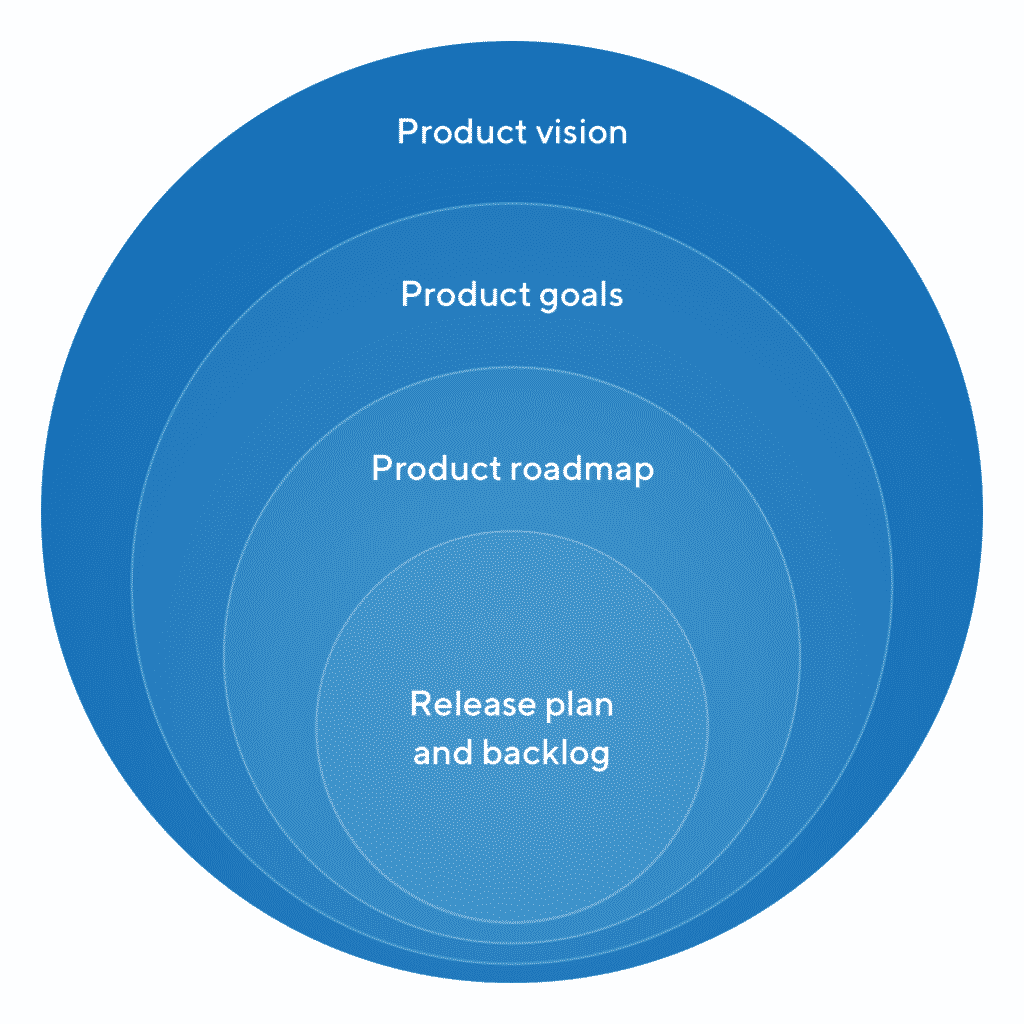
Crafting a Successful Roadmap for Agile Teams
A roadmap is a crucial navigational tool that aligns a team around measurable goals rather than a static list of features. It is a strategic instrument that goes beyond the conventional feature-based timeline, focusing instead on solving tangible problems that deliver real value to users and stakeholders. By orienting the team around outcome-driven goals, the roadmap fosters an adaptive, customer-focused mindset that is receptive to feedback and flexible in its execution. It allows Agile teams to anticipate and respond to change, prioritize work that advances key performance indicators, and develop a deeper understanding of customer needs. When constructed with a clear vision, the roadmap acts as a communication bridge between diverse stakeholders, ensuring transparency, setting realistic expectations, and providing a holistic view of the strategic direction. This approach encourages continuous refinement and reassessment, ensuring the team remains focused on delivering tangible, value-driven solutions rather than adhering strictly to a prescriptive feature set.
To masterfully navigate through the complexities of roadmap development and execution in an agile context, Lean Agile Intelligence provides a structured framework divided into the stages of Developing, Emerging, Adapting, and Optimizing. This tiered approach offers a sequential pathway for teams to enhance their understanding and application of roadmap strategies, aligning their work with broader business goals and user requirements. Each stage delves into different facets of roadmap planning and execution, presenting tailored improvements and techniques that evolve with the team's maturity. From establishing a fundamental understanding and creating initial roadmaps to refining and optimizing these strategic plans, the framework ensures that teams are equipped with the necessary tools and insights at each step. This progressive learning journey empowers teams to create and maintain roadmaps that are both flexible and outcome-focused, enabling them to deliver solutions that genuinely resonate with customers and drive business success.
Developing
Teams “developing” an understanding of the value of the Roadmap and adopting the foundational techniques should focus on the following improvements.
- The What: A Roadmap exists that includes both technical enablers (i.e., Infrastructure work) and customer-facing features for at least the next 12 months
- The How: Creating a comprehensive and forward-looking roadmap is a complex process that requires collaboration across different departments. To achieve this, teams must break down silos and integrate diverse perspectives and expertise from developers, operations, infrastructure, customer service, and finance. This inclusive approach ensures the roadmap balances addressing technical debt and infrastructural work and introducing new features to create a strong foundation for sustainable long-term development. The roadmap should be treated as a living document that can be adjusted and refined based on market conditions, customer feedback, and technical realities. It should stretch at least 12 months into the future and serve as a strategic guide to align diverse departments around a shared vision. This helps ensure all stakeholders understand their role in achieving future-ready solutions and facilitates a proactive approach to addressing opportunities and challenges.
- The What: The Roadmap is routinely updated to reflect changes and work in progress
- The How: Regularly updating a roadmap is crucial, especially in Agile environments, because it differs fundamentally from a project plan. While a project plan is a fixed document with specific tasks, responsibilities, and timelines to achieve a particular outcome, a roadmap is a flexible guide that explains broad objectives, critical problems to solve, and the direction of the product or service over time.
- As the market and technological landscape changes, customer needs, competitive pressures and internal capabilities shift, sometimes unpredictably. Therefore, a roadmap must be dynamically updated to reflect these changes, allowing an organization to pivot or adjust its strategies effectively. Continuously evolving, the roadmap remains relevant and valuable, offering clear guidance on strategic priorities while avoiding becoming outdated documents that no longer reflect reality. This practice reinforces the principle of 'responding to change over following a plan,' one of the core values of Agile. By keeping the roadmap current, teams can stay aligned with the overall strategy and vision, fostering a work culture that is responsive and adaptable rather than just ticking off tasks on a predetermined list. It helps prevent the disconnect between daily activities and strategic objectives, ensuring everyone moves in the right direction even as specifics may change.
- This article by Roman Pichler describes a great template to get started with called a Goal Oriented Product Roadmap.
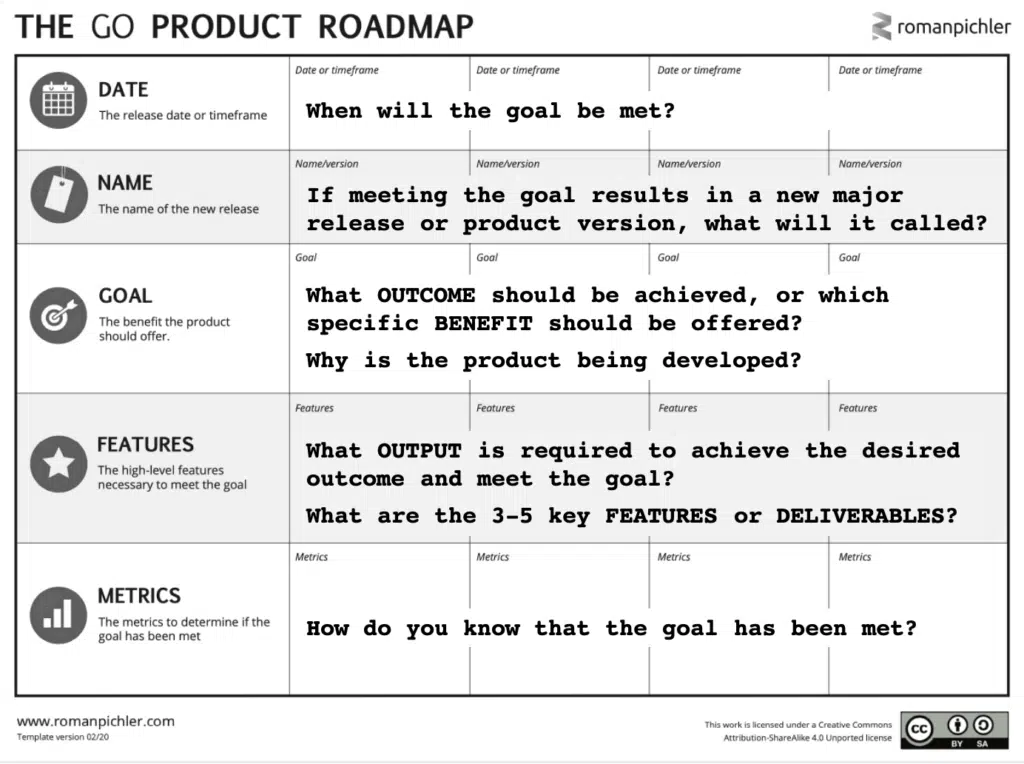
- The What: The Roadmap is transparent to all stakeholders.
- The How: Transparency with stakeholders is paramount regarding roadmaps, as it builds trust, ensures alignment, and fosters informed decision-making throughout the organization. A transparent roadmap clarifies the strategic direction, justifies why certain decisions are made and sets realistic expectations regarding deliverables, timelines, and the impact on business objectives. Here are some tips to achieve roadmap transparency:
-
Regular Communication and Updates: Establish consistent communication channels to share updates on the roadmap. This could be through regular newsletters, dedicated Slack channels, or periodic stakeholder meetings. Updating stakeholders about changes, progress, or shifts in priorities keeps everyone informed and aligned.
-
Accessible Documentation: Make the roadmap accessible to all relevant parties, possibly through a shared digital platform, a visual display in common areas, or collaborative cloud-based tools. When stakeholders can view the roadmap at their convenience, it enhances transparency and inclusion.
-
Visual Representation and Simplicity: Create a visual, easy-to-understand roadmap representation. Utilizing charts, graphs, and timelines can help stakeholders digest information better than text-heavy documents. Simplifying the content to include just the key elements makes it easier for everyone to understand the big picture, regardless of their role.
-
Feedback Mechanisms: Encourage and facilitate feedback from stakeholders. This could be through regular surveys, feedback boxes, or interactive Q&A sessions during roadmap presentations. When stakeholders know their input is valued and considered, it creates a culture of openness.
-
Honesty about Uncertainties and Risks: Be candid about the uncertainties, assumptions, and risks inherent in the roadmap. Acknowledging and discussing these aspects prevents unrealistic expectations and shows stakeholders that while the direction is clear, flexibility is necessary for dealing with the unpredictable nature of business and technology landscapes.
-
Education and Support: Educate stakeholders about Agile principles and the roadmap's purpose. Workshops, seminars, or informal lunch-and-learns could serve this purpose. When stakeholders understand that a roadmap is a strategic guide — not an unchangeable plan — they are more likely to appreciate the updates and changes that come with it.
-

Emerging
Teams “emerging” beyond the foundational techniques of the Roadmap and embracing it as they become more proficient should focus on the following improvements.
-
The What: The Roadmap connects to a release cadence and shows delivery targets.
- The How: Connecting a roadmap to a release cadence and displaying delivery targets is crucial for maintaining a rhythm of predictable and reliable deliveries, which instills confidence among stakeholders and team members. This practice ensures that the team's efforts align with strategic objectives and that there's a clear understanding of what is achievable within each timeframe, thereby setting realistic expectations.
Linking the roadmap to specific release cadences is crucial for aligning team efforts with business milestones, managing stakeholder expectations, and fostering a reliable atmosphere within the organization. This strategic approach sets realistic expectations by visually demonstrating the correlation between planned features and business timelines, thereby mitigating the risk of overcommitment and instilling a sense of predictability and trust. Stakeholders and customers are more adept at planning and are reassured by the consistent rhythm at which new functionalities or enhancements are delivered. Moreover, by making delivery targets explicit, teams maintain a sharp focus on the imperative of value delivery, ensuring prioritization that resonates with the customers' needs and expectations, and guarantees that the most beneficial and impactful tasks are addressed promptly. This comprehensive strategy fortifies the organization's reliability and commitment to its strategic objectives.
-
-
-
Visualize the Cadence: Create a visual representation of the roadmap that highlights the release cadence. Use different colors or symbols to differentiate between various types of releases (major, minor, patches) and include tentative dates for each planned release.
-
Regular Reviews and Adjustments: Conduct routine roadmap reviews to adjust plans based on the team’s velocity, business priorities changes, or stakeholder feedback. Regular updates to the roadmap ensure it reflects the most accurate, up-to-date plans and expectations.
-
Communicate Changes Proactively: If there are any changes in the release cadence or delivery targets, communicate these changes to all stakeholders as soon as possible. Provide a rationale for the change and its expected impact, maintaining transparency and trust.
- Integrate Feedback Loops: Incorporate feedback from stakeholders and team members into the roadmap process. Use past-release insights to refine the process and engage in continuous dialogue to ensure the roadmap remains aligned with stakeholder needs and expectations.
-
Use Roadmap Software with Timeline Features: Employ a roadmap tool that supports timeline views and can easily be updated. These tools often include features for tracking progress toward delivery targets and can be shared with or viewed by stakeholders.
-
-
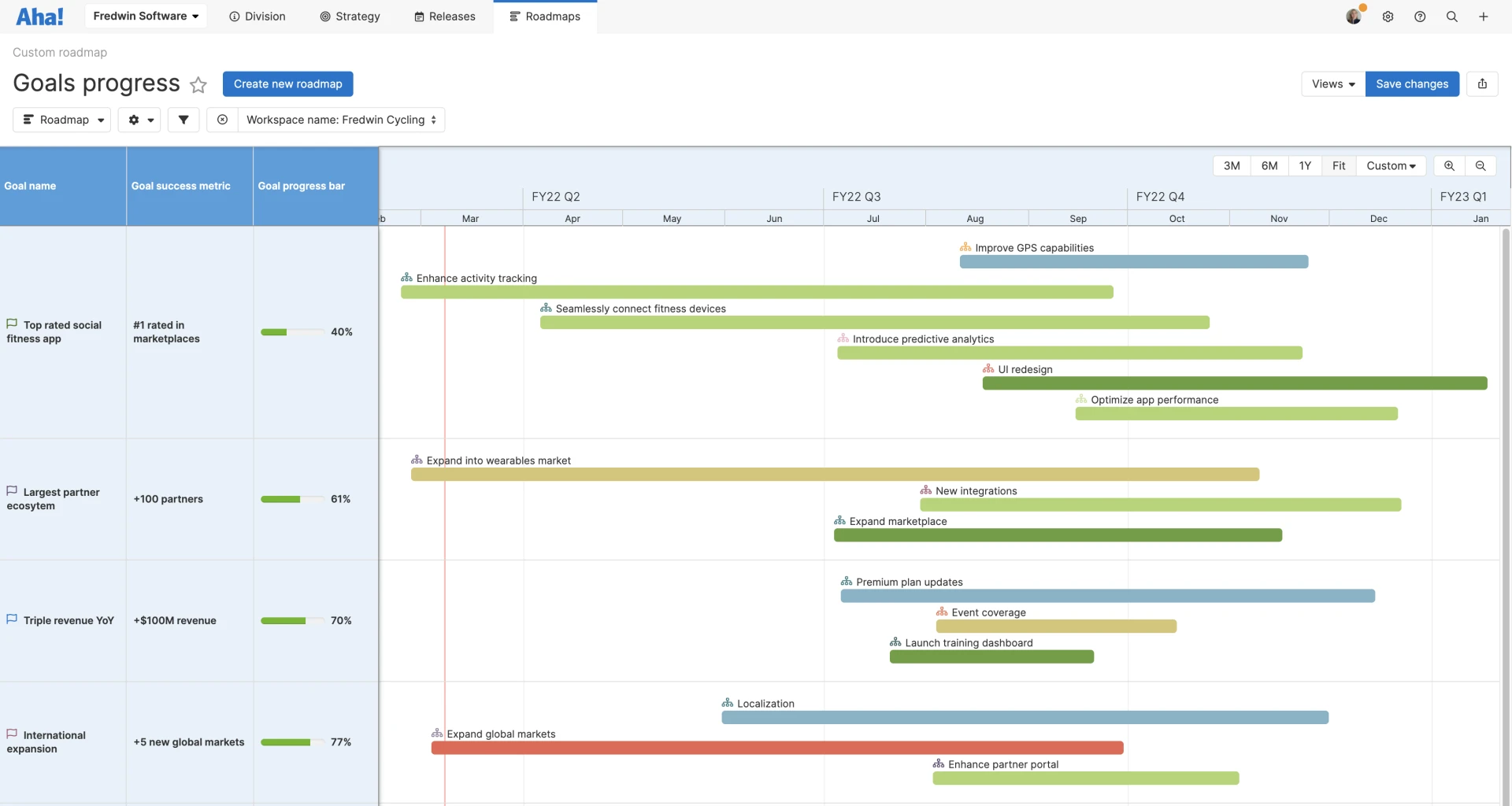
Timeline view with goals via Aha.
Adapting
Teams “adapting” beyond the foundational techniques of the Roadmap and embracing it as they become more proficient should focus on the following improvements.
- The What: The Roadmap is referenced when discussing priorities and capacity constraints with stakeholders.
- The How: Referencing the roadmap during discussions about priorities and capacity constraints with stakeholders is essential because it grounds these conversations in reality, ensuring everyone is on the same page about what is achievable given current resources and timelines. This practice helps prevent overcommitment on tasks and fosters a more realistic approach to what can be delivered, enhancing the credibility of the team and trust among stakeholders. To achieve this, it's advisable to have regular meetings where the roadmap is visibly used as a guiding document, such as a Sprint Review, System Demo, etc. During these sessions, openly discuss the reasoning behind the scheduling, the resources available, and how various tasks have been prioritized. This continuous reference to the roadmap reinforces its significance as a strategic tool. It ensures that all decisions are aligned with the broader goals and constraints, keeping stakeholder expectations in check and strategic initiatives on track.
- The What: Team members can articulate the reason why things are ordered the way they are (i.e., value, capacity constraints)
- The How: It's critically essential for agile team members to understand and articulate the reasoning behind the order of their work items, such as value delivery and capacity constraints, as this comprehension anchors their daily efforts in broader strategic goals and ensures that they are not just executing tasks, but moving forward with purpose and priority. This clarity enhances team autonomy, motivation, and the ability to make quick, informed decisions, especially in dynamic environments where priorities may shift rapidly. Leaders and product owners should ensure the 'why' behind the work order is transparent and openly discussed to make this possible. This can be achieved through methods such as:
- Regularly holding collaborative prioritization sessions, like backlog refinement meetings, where the rationale for sequencing work items is explained in the context of business value and current constraints.
- Encouraging a culture of open inquiry, where team members are welcomed and expected to ask questions about the priority of their work during daily standups or other team meetings, ensuring everyone is aligned and has clarity.
- Providing clear criteria for prioritizing work, using frameworks that consider value delivery, risk, capacity, and dependencies, and offering team members a clear lens through which they can view and understand decision-making.
- Training and ongoing education about agile and lean thinking principles ensure that team members are equipped to understand decisions and contribute meaningfully to the prioritization process.
- The How: It's critically essential for agile team members to understand and articulate the reasoning behind the order of their work items, such as value delivery and capacity constraints, as this comprehension anchors their daily efforts in broader strategic goals and ensures that they are not just executing tasks, but moving forward with purpose and priority. This clarity enhances team autonomy, motivation, and the ability to make quick, informed decisions, especially in dynamic environments where priorities may shift rapidly. Leaders and product owners should ensure the 'why' behind the work order is transparent and openly discussed to make this possible. This can be achieved through methods such as:
Optimizing
Teams “optimizing” beyond the foundational techniques of the Roadmap and embracing it as they become more proficient should focus on the following improvements.
- The What: The Roadmap contains goals and outcomes of the product, not necessarily features.
- The How: The product roadmap is a pivotal instrument within product management, though its effective utilization presents considerable challenges. A common pitfall is the roadmap's tendency to concentrate predominantly on specific features, leading to difficulties in reaching consensus and fostering alignment. This feature-centric approach can yield a roadmap that is not only excessively detailed but also susceptible to frequent alterations. To maintain an outcome-oriented roadmap rather than solely scope-based, it is imperative to integrate strategies that underscore broader objectives and measurable results. This involves setting clear, value-driven goals at the outset that resonate with stakeholders' and customers' primary needs and challenges. Encourage regular dialogues that steer the conversation away from feature specifics and toward the benefits and outcomes that those features aim to achieve. By visualizing the end-state solutions or improvements the product seeks to bring, teams can create roadmaps that remain adaptable and resilient to market or customer preferences changes. A thematic approach to road mapping, where themes are based on outcomes rather than specific features, can further ensure that the product's direction aligns with its long-term strategic goals, facilitating a more flexible and pivot-ready planning process.
Conclusion
In essence, the creation and implementation of a roadmap within an agile environment is a strategic endeavor that transcends mere task management and feature listing. It involves a holistic view that integrates the technical aspects of product development with a keen understanding of customer needs and business objectives. As agile teams progress through the phases of Developing, Emerging, Adapting, and Optimizing their roadmaps, they cultivate an environment that prioritizes adaptability, strategic foresight, and customer-centricity. A well-structured roadmap serves as a beacon, guiding teams in their journey towards delivering impactful, value-driven solutions. It is a dynamic tool that facilitates communication, alignment, and transparency across all stakeholders, ensuring that every effort contributes meaningfully to the broader organizational goals. By continuously refining their roadmaps, agile teams can respond adeptly to changing market demands and technological advancements, ensuring that their products and services remain relevant, competitive, and aligned with their user base's evolving needs. To gain a comprehensive understanding of your team's current process status, we recommend taking advantage of our free agile assessment for Team Agility.